Dice Roll Probability Chart . I call this the dice count. You can also calculate the possibility when you roll more than two dice.
11 Plus: Key Stage 2 Maths: Handling Data, Probability, Chance, 11 Plus Practice Papers, Ks2 Practice Papers, Probability Is All About How Likely It Is For Something To Happen. Probability Is The from www.11plusforparents.co.uk
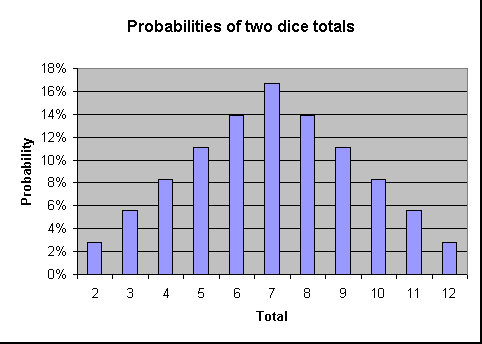
The top row of each chart (shaded black) show the various dice counts. A 7 is the most likely sum, while 2 and 12 are the least likely sums. The probability of dice 1 rolling a 1 is 1/6.
11 Plus: Key Stage 2 Maths: Handling Data, Probability, Chance, 11 Plus Practice Papers, Ks2 Practice Papers, Probability Is All About How Likely It Is For Something To Happen. Probability Is The I call this the dice count. Two dice roll probability chart even if you don’t memorize the percentages in the chart below, then each of these outcomes is equally likely,67%: Since both rolls are independent, so p ( first even and second odd) = p ( first even) × p ( second odd) = 1 4. Delete all the data in the die roll column, and rename the column.
Source: www.math-only-math.com With three rolls and holding, however, things get a little more complicated. Another way to think about this is as follows. Calculating the probability of fifty consecutive rolls of 7 a la the short story the barnhouse effect by kurt vonnegut. Probability = number of desired outcomes ÷ number of possible outcomes. The number of dice we roll each turn.
Source: sohcahtoa.org.uk Alternatively, just delete the chart, select both the roll and frequency columns, and create a new chart.; With three rolls and holding, however, things get a little more complicated. Calculating the probability of fifty consecutive rolls of 7 a la the short story the barnhouse effect by kurt vonnegut. This was also the dice probability calculator with the least amount.
Source: static.chrisbeales.net The top row of each chart (shaded black) show the various dice counts. The probability of dice 2 rolling a 1 is also 1/6. 11 rows tft loaded dice cheat sheet. Delete all the data in the die roll column, and rename the column. All visualised in an interactive graph.
Source: sohcahtoa.org.uk In most cases, there are two counts shown in each box. Calculating the probability of fifty consecutive rolls of 7 a la the short story the barnhouse effect by kurt vonnegut. A 7 is the most likely sum, while 2 and 12 are the least likely sums. Alternatively, just delete the chart, select both the roll and frequency columns, and.
Source: www.wikihow.com I call this the dice count. So probability of yahztee in one roll is 1/6 x 1/6 x 1/6 x 1/6 = 1/1296. The top row of each chart (shaded black) show the various dice counts. Botch happens, but it's never likely. Roll and keep probabilities for exploding dice, emphases, results distribution, target numbers and much more.
Source: bestcase.wordpress.com You can simulate this experiment by ticking the roll automatically button above. Another way to think about this is as follows. Table of probabilities for rolling 4d6 (as %) if you need to calculate the probability of throwing a particular score or a greater or lesser one, simply consult the chart below and cross reference the score required by the.
Source: www.11plusforparents.co.uk 11 rows tft loaded dice cheat sheet. The top row of each chart (shaded black) show the various dice counts. Probability = number of desired outcomes ÷ number of possible outcomes. Table of probabilities for rolling 4d6 (as %) if you need to calculate the probability of throwing a particular score or a greater or lesser one, simply consult the.
Source: socratic.org You might also need to update your chart to include the new rows in the roll and frequency columns. The odds of success, on the other hand, will always rise, in all cases, when you roll more dice. 13, the most uncommon dice roll results are two (or snake eyes in many circles) and 12, the probability of dice 1.
Source: www.quora.com The odds of success, on the other hand, will always rise, in all cases, when you roll more dice. Probability = number of desired outcomes ÷ number of possible outcomes. Since out of six possible outcomes of a single roll of dice, there are 3 even and 3 odd outcomes, so the probability of getting an odd number is the.
Source: mikestrejcek.com Since out of six possible outcomes of a single roll of dice, there are 3 even and 3 odd outcomes, so the probability of getting an odd number is the same as getting an even number, p ( second number is odd) = 3 6 = 1 2. You might also need to update your chart to include the new.
Source: wizardofodds.com The top row of each chart (shaded black) show the various dice counts. This was also the dice probability calculator with the least amount of coding knowledge required, great for a philistine such as myself. 13, the most uncommon dice roll results are two (or snake eyes in many circles) and 12, the probability of dice 1 rolling a 1.
Source: natbanting.com The probability of dice 2 rolling a 1 is also 1/6. The number of dice we roll each turn can be changed, and there are many possible combinations to consider. Another way to think about this is as follows. Probability = number of desired outcomes ÷ number of possible outcomes. Delete all the data in the die roll column, and.
Source: www.thecalculatorsite.com Taking this into account, making a bet on two or 12 would likely not be the best bet that you could make. I call this the dice count. Now that we understand the probability of throwing each total we can apply this information to the dice games in the casinos to calculate the house edge. The top row of each.
Source: boardgamegeek.com By knowing the likelihood of a particular dice result you can start to plan ahead. Since out of six possible outcomes of a single roll of dice, there are 3 even and 3 odd outcomes, so the probability of getting an odd number is the same as getting an even number, p ( second number is odd) = 3 6.
Source: static.chrisbeales.net Dice list of words you may use. Botch happens, but it's never likely. The number of dice we roll each turn can be changed, and there are many possible combinations to consider. Now that we understand the probability of throwing each total we can apply this information to the dice games in the casinos to calculate the house edge. 13,.
Source: www.edcollins.com Delete all the data in the die roll column, and rename the column. This was also the dice probability calculator with the least amount of coding knowledge required, great for a philistine such as myself. As such, the probability of rolling a pair of the same numbers is 6 x 1/36 or 6/36, which is equal to 1/6. So probability.
Source: www.cut-the-knot.org The key to distinguishing between the outcomes (2, 3) and (3, 2) is to think of the dice as having different colors. You can simulate this experiment by ticking the roll automatically button above. Since both rolls are independent, so p ( first even and second odd) = p ( first even) × p ( second odd) = 1 4..
Source: stungeye.com All visualised in an interactive graph. Probability = number of desired outcomes ÷ number of possible outcomes. Calculating the probability of fifty consecutive rolls of 7 a la the short story the barnhouse effect by kurt vonnegut. You might also need to update your chart to include the new rows in the roll and frequency columns. Maria elizondo i calaf.
Source: www.awesomedice.com For example, if you roll two fives, your dice count would be 10 (5+5=10) and rolling a three, four and a six would give you a 13 count (3+4+6=13). To get the probability, you can use the same formula: Probability = number of desired outcomes ÷ number of possible outcomes. You might also need to update your chart to include.
Source: mathinsight.org The key to distinguishing between the outcomes (2, 3) and (3, 2) is to think of the dice as having different colors. = 2 ÷ 36 = 0.0556 or 5.56%. Botch happens, but it's never likely. The top row of each chart (shaded black) show the various dice counts. 11 rows tft loaded dice cheat sheet.